
As of September 20, the global death toll surpassed 957,000 amid more than 30.8 million cases. Over 21 million people have recovered from the disease worldwide, according to the data collected by the Johns Hopkins University in the United States.
KEEP READING
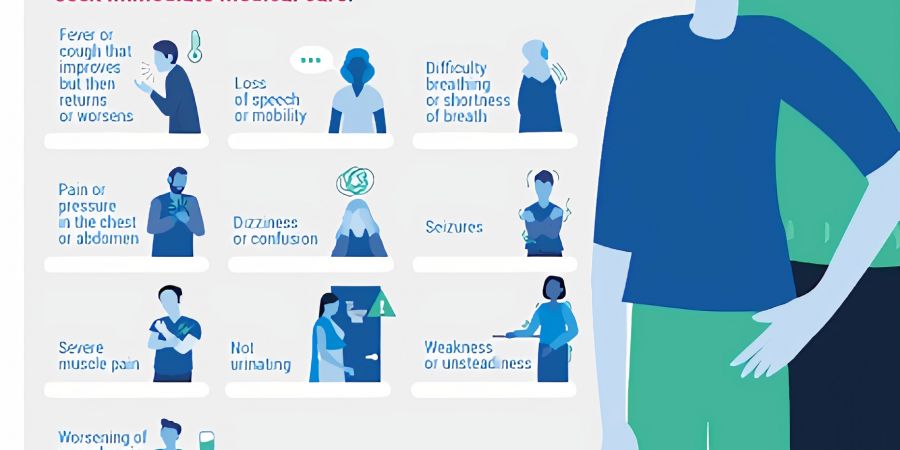
Coronavirus: All you need to know about symptoms and risksHow does coronavirus spread and how can you protect yourself?Coronavirus: Which countries have confirmed cases?
Here is what you need to know:
The coronavirus family causes illnesses ranging from the common cold to more severe diseases such as severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), according to the WHO.
They circulate in animals and some can be transmitted between animals and humans. Several coronaviruses are circulating in animals that have not yet infected humans.
The new coronavirus, the seventh known to affect humans, has been named COVID-19.
Coronavirus: Italy to close all schools and universities (2:19)
Common signs of infection include fever, coughing and breathing difficulties. In severe cases, it can cause pneumonia, multiple organ failure and death.
The incubation period of COVID-19 is thought to be between one and 14 days. It is contagious before symptoms appear, which is why so many people get infected.
Infected patients can be also asymptomatic, meaning they do not display any symptoms despite having the virus in their systems.
China alerted the WHO to cases of unusual pneumonia in Wuhan on December 31.
COVID-19 is thought to have originated in a seafood market where wildlife was sold illegally.
On February 7, Chinese researchers said the virus could have spread from an infected animal to humans through illegally trafficked pangolins, prized in Asia for food and medicine.
Scientists have pointed to either bats or snakes as possible sources.

The WHO declared the virus a pandemic on March 11 and said it was “deeply concerned by the alarming levels of spread and severity” of the outbreak.
The WHO recommends basic hygiene such as regularly washing hands with soap and water, and covering your mouth with your elbow when sneezing or coughing.
Maintain “physical distancing” – keeping at least 1 metre (three feet) between yourself and others – particularly if they are coughing and sneezing, and avoid touching your face, eyes and mouth with unwashed hands.
Avoid unnecessary, unprotected contact with animals and be sure to thoroughly wash hands after contact.




