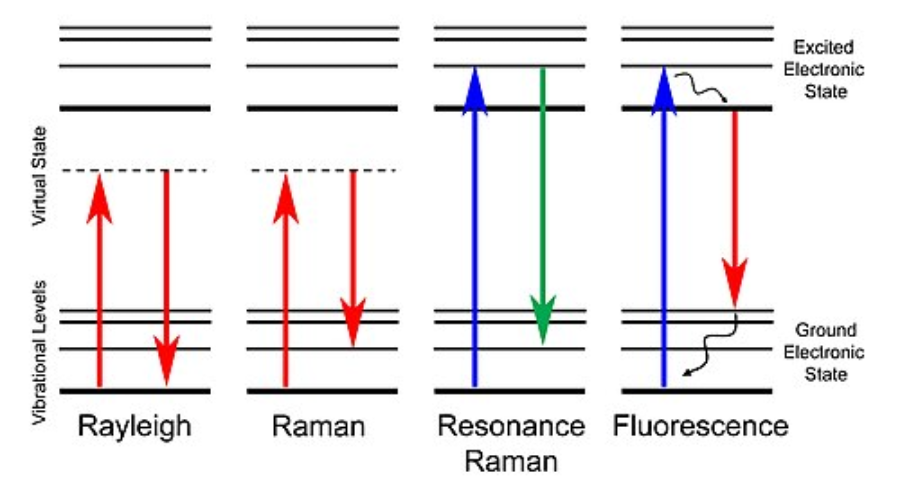
Raman effect: When an intense beam of monochromatic light is passed through on organic liquid,the light gets scattered by the molecules of the liquid.the scattered light can be observed through a spectroscope in a direction perpendicular to the incident beam.The scattered beam is found to consist of light of the same wavelength as the incident light as well as light of longer wavelength and shorter wavelength then the incident light.The incoherent scattering of light in which the scattered light has slightly different frequencies from that of incident light and there is a change of atomic oscillations within the molecules is as the RAMAN EFFECT.This phenomenon was first noticed and studied by sir C.V.RAMAN in 1928.The spectrum of the scattered light is known as RAMAN SPECTRUM.
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY: The apparatus consists of a Glass tube(G),closed at one end by the an optically plane glass plate.The other end is drawn in the form of a horn (H) whose outer surface is well blackened to provide a suitable background.The tube contains the liquid (sample) under study.It is surrounded by a constant temperature bath (W).The liquid is irradiation by light from a powerful mercury lamp (S). The light is rendered monochromatic by passing it through a suitable filter (F) which filters out all the colours except the blue colour of wavelength 4358A°.
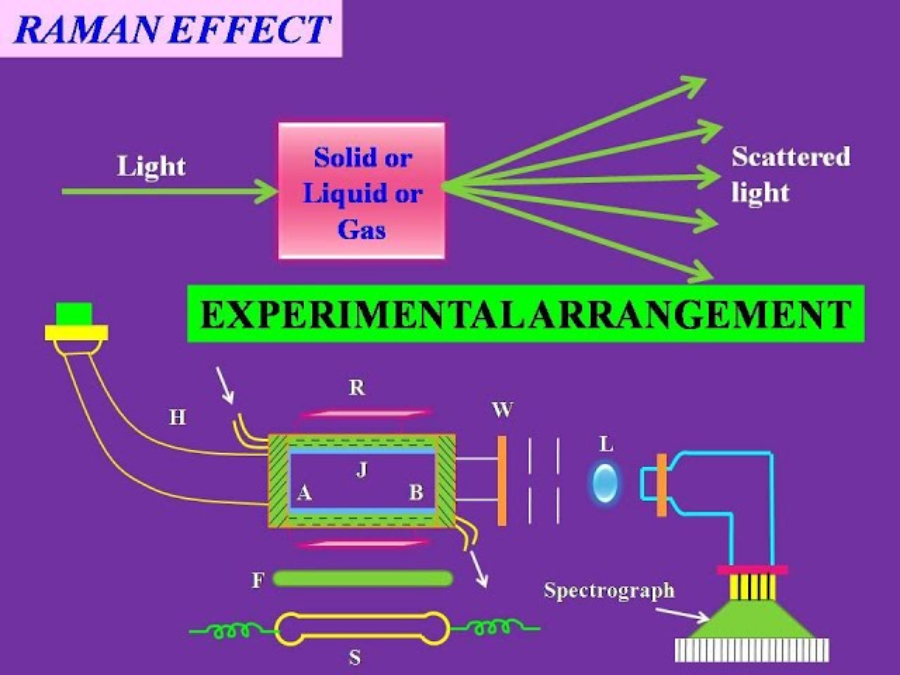
The intensity of the light is increased by keeping the source close to the tube and also using an aluminium concave reflector. The essential features of a good Raman spectrograph are :
1. Large light gathering power. 2. Special prism of high resolving power. 3.A short focus camera.
The light incident on the liquid is viewed axially with help of a suitable prism.The light is received in a powerful spectroscope having large light gathering power and high resolving power.After adjusting the arrangement for the best fit,The telescope of the spectrometer is replaced by a photo graphic camera. After sufficient exposure,the photo flim is developed and the various Raman lines are obtained in the flim. The Raman spectrum consists of an intense line whose wavelength is the same as the wavelength of the incident light.This intense spectral line is known as the parent line.There lines on either side of the parent line.The lines of longer wavelength are stokes lines.The lines of shorter wavelength are known as anti Stoke lines.All the above lines are known as the Raman lines. The graph is obtained by the various lines as shown in fig: