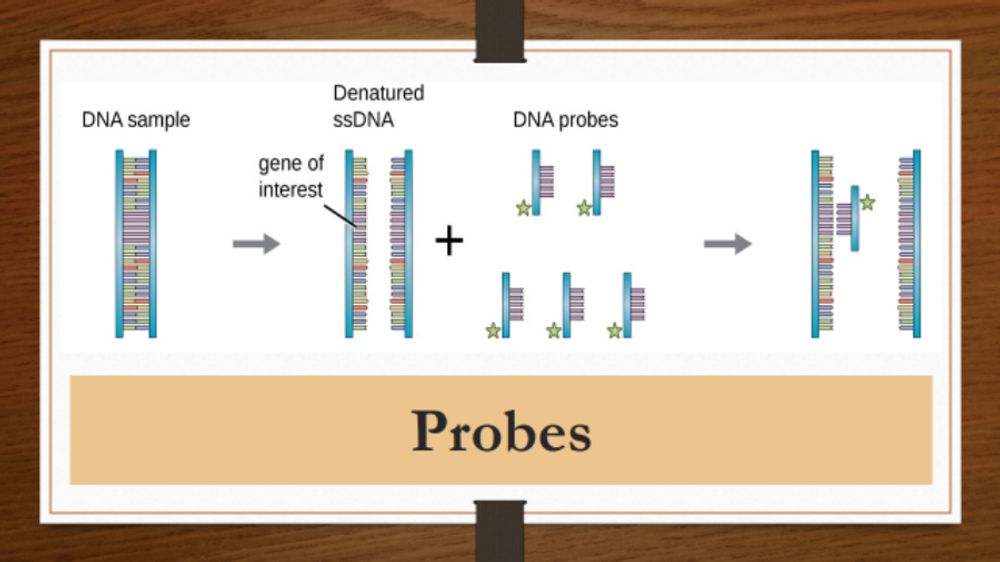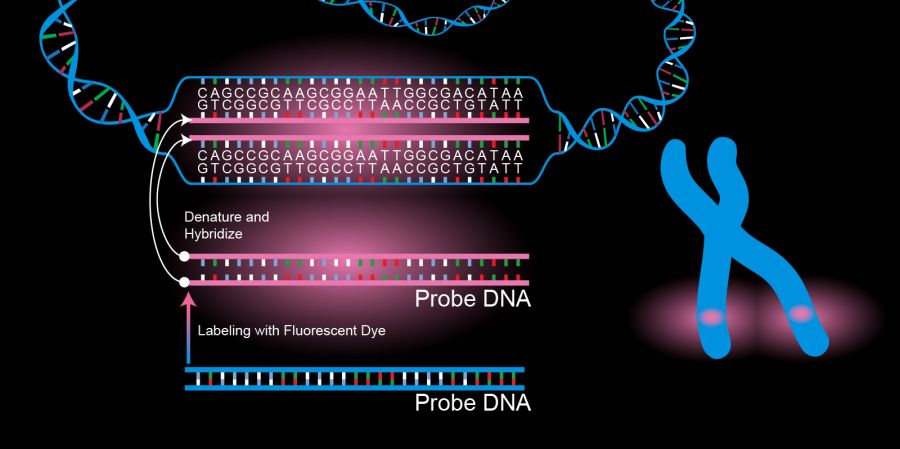
DNA probes: The specificity of the interaction in base pairing DNA or RNA synthesis enable the production of specific DNA probes.These are radioactive,biotinylated or other wise labelled copies of cloned single stranded DNA fragments, usually 20-25 nucleotide long and containing unique nucleotide sequence which can be used for the detection of homologous DNA by hybridization.DNA probes are being used increasingly in the diagnosis of infectious disease.Probes containing sequence unique to the microbes to be detected can be added to microbial culture,body fluids, tissue or other material suspected to contain the microbes or its DNA.The DNA probes hybridises with the complementary specific sequence on the microbes The advantage of DNA probes for diagnosis are their high degree of specificaty, ability to detect minute quantities of complementary DNA even in the presence of other microbes, and the capacity to recognise microbes that are either difficult or impossible to culture.DNA probes for the detection of many pathogens are now commercially available.
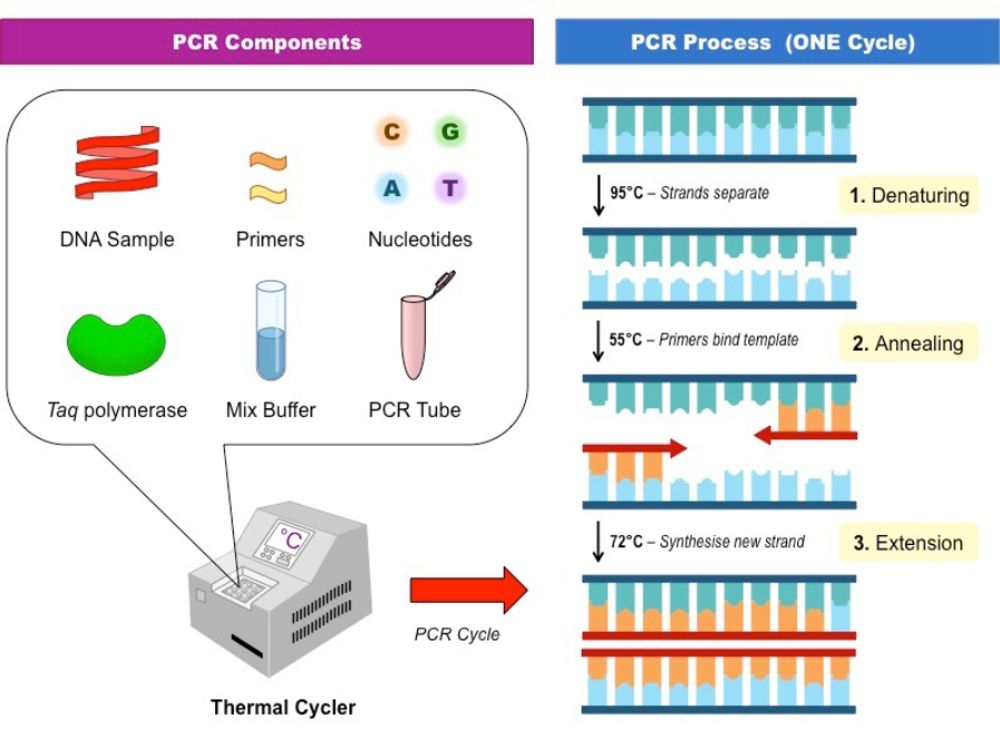
Polymerase chain reaction:
This is a rapid automated method for the amplification of specific DNA sequence , invented by kary B mullis in 1983, for which he won the Nobel prize in chemistry in 1993.PCR consist of several cycle of sequential DNA replication where the products of the first cycle become the template for the next cycle.It make available abundanct quantities of specific DNA sequence starting from source containing minimal your time to quantities of the same.With it.'s enormous capacity to amplify DNA,PCR is a versatile tool useful in diverse areas suchspend thank you. as diagnosis of infectious, genetics or neoplastic disease,in Thank you all for yoforensic investigation,in archaeobiological studies of ancient specimen and in the examination of phylogenetic relationships in evolution.Based on the principle of PCR, others target amplification system have een developed.One such, transcription mediated amplification,which amplifies ribosomal RNA instead of DNA,has been applied as a rapid diagnostic techniques for infection such as tuberculosis where culture are difficult or delayed.
Restrictions endonucleases: These are microbial enzyme which cleave double stranded DNA at specific oligonucleotide sequences.Many such enzyme have been recognised.he natural function of restrictions enzyme in bacteria may be destruction of foreign DNA that may enter the bacterial restrictions enzyme split DNA strand into fragments of varying lengths.These can be separated by gel electrophoresis and stained with ethidium bromide and photographed.