

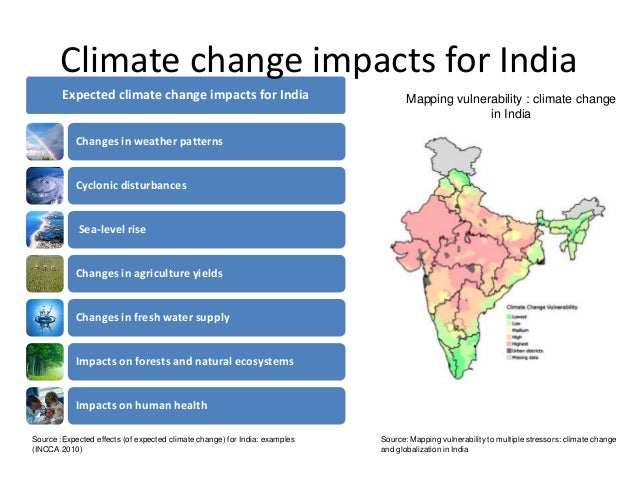
INDIA has been facing the brunt of climate change in various parts of the country. Excessive rainfall, floods, cyclones, and severe droughts occur often. The economic survey 2017-18 cited a decline in the annual rainfall in India in the last three decades. it impacted adversely on the agricultural crops and GDP of our country. India ranked at 4th position in the 2017 German report on climate changed for the most vulnerable country. The world bank estimates that by 2030, India will require $2.5 trillion to deal with climate change. however, Climate change has a huge economic and socio-political impact, threatening our food and energy security, lead water scarcity, floods, and atmospheric pollution, and disease.
fortunately, India takes the lead among the developed countries in de-carbonizing itself and adopting climate-resilient technologies. India needs to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture, forestry, and land use. Reducing coal consumption is a must because still, many people in a rural area or backward area prefer the use of coal for cooking rather than, gas cylinders or gas pipelines or also there are so many uses of coals which India needs to stop. Fossil fuel-free energy systems and investment in energy efficiency will help to develop alternate strategies for development.
India has come up with an elaborate policy framework. Measures are being taken for replacing fossil fuels with non-fossil fuel up to 40% by 2030. the government will create more forest cover by 2030. A national action plan was created in 2008 by the Prime minister's council on climate change which is focusing on 8 missions. All states and UTs will coordinate in the formulation of action plans for the adaptation. As PM Modi said, “there must be a paradigm shift in global attitude towards climate from ‘carbon credit to green credit’ to improve the quality of life of its citizens”.
India has designed 4 new national missions:-
Or, NAPCC report 2018, highlighted 8 missions that cover the increase in the use of solar energy, improving energy efficiency, sustainable urban planning, and sustainable infrastructures like buildings, waste management, water resources, and transportation. water will be conserved by decreasing waste and ensuring equitable distribution of water. A comprehensive knowledge system for climate change will be put in place as part of the action plan for climate-resilient agriculture. the focus will be on climate-resilient ecosystems, biodiversity, water preservation, biomass, mangroves, wetlands, and most important the Himalayan ecosystem.






























