
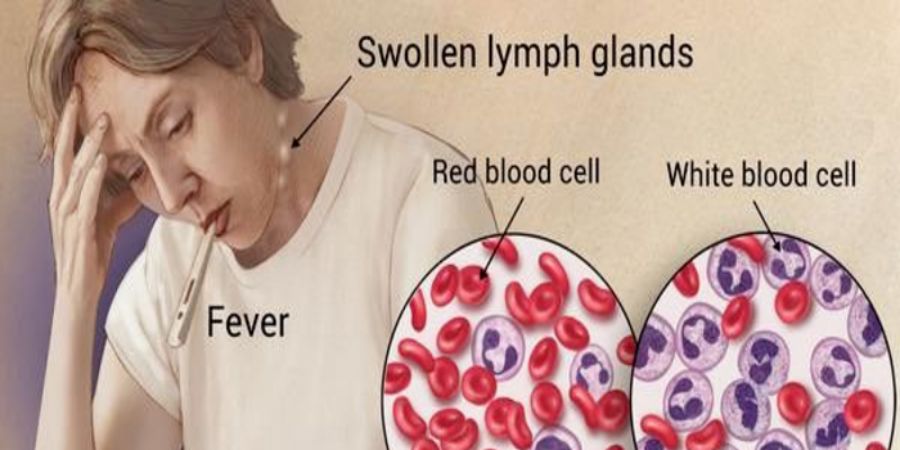
HELLO WORLD…… In this blog, I have come forward to talk about leukemia. The majority of incidences of this disease occur in older people. I have tried my part to provide adequate information regarding the illness and their groupings. Let us proceed….
Morphogenesis is defined as the arising of hemoblastoses when a single stem cell becomes malignant, resulting in a pool of tumor cells. This indicates that all hepatoblastomas are monoclonal. A Philadelphia chromosome, for example, can be found in all tumor cells in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Stem cells make up about 0.01-0.001 percent of the total number of cells in the bone marrow. Development factors and the stromal milieu influence stem cell growth and differentiation. Experiments with cell cultures show that the growth and differentiation of cells can only occur in the presence of growth agents.
Hemoblastosis is a type of hematopoietic tumor that is split into two types: leukemia [systemic tumor illness of the lymphatic tissues] and lymphomas [regional tumor diseases of the lymphatic tissue].
LEUKEMIA [ LEUKAEMIA ] :
It is characterized by the increasing growth of leukemia cells. They begin in the hematological system and subsequently spread hematogenously to different organs and tissues, generating leukemia infiltrates. Leukemia is thought to be a polyethological illness, meaning that numerous variables contribute to its development. There are three major types: viruses, ionizing radiation, and chemicals. Scientific study has established the function of viruses in the development of leukemia. Ionizing radiation can induce radiation leukemia, and the frequency of mutations is affected by the amount of ionizing radiation. Among the most dangerous substances include dibenzanthracene, benzopyrene, methylcholanthrene, and others.
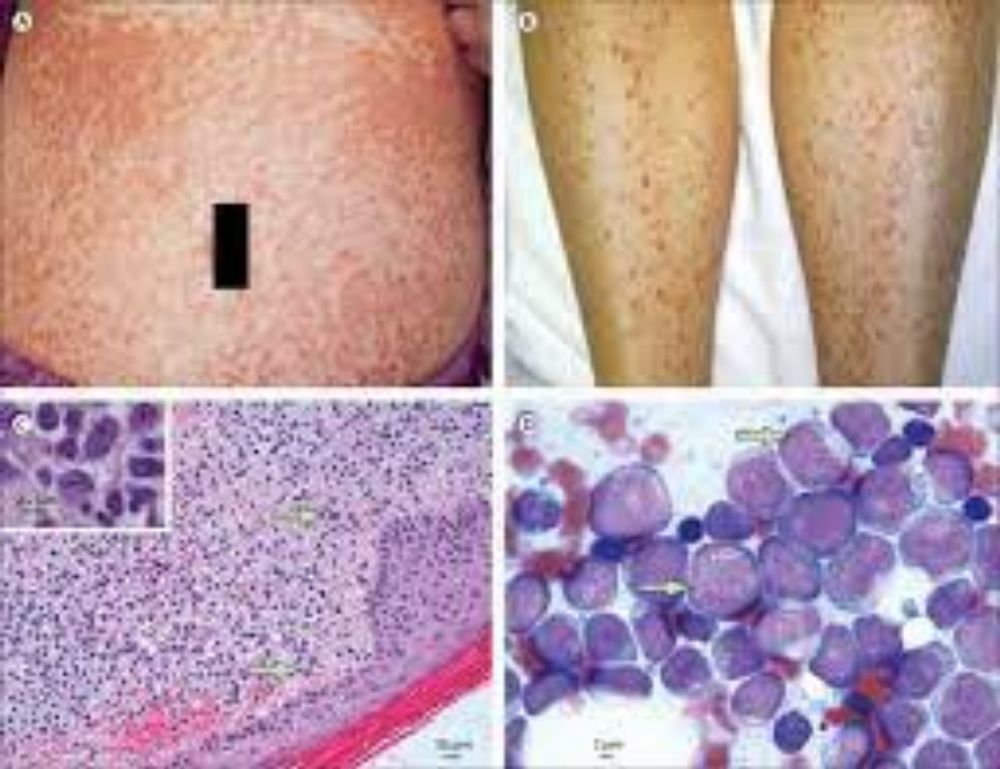
ACUTE LEUKAEMIA: Acute leukemia is distinguished by the development of blast cells in the bone marrow and peripheral circulation- the leukemia gap[a sharp increase in the number of blasts and single mature elements in the absence of transitional form]. A frequent symptom of acute leukemia is an enlarged liver and spleen, as well as bone marrow in long and flat bones that are red, juicy, and sometimes grey. Hemorrhages in the mucous and serous membranes, organs, and tissues may occur, which are exacerbated by ulcerative necrotic processes and sepsis. The cytochemical features and appearance of the cells help to provide a more accurate diagnosis of the kind of leukemia. The morphology of acute leukemia is based on the Bone Marrow Insufficiency Syndrome.
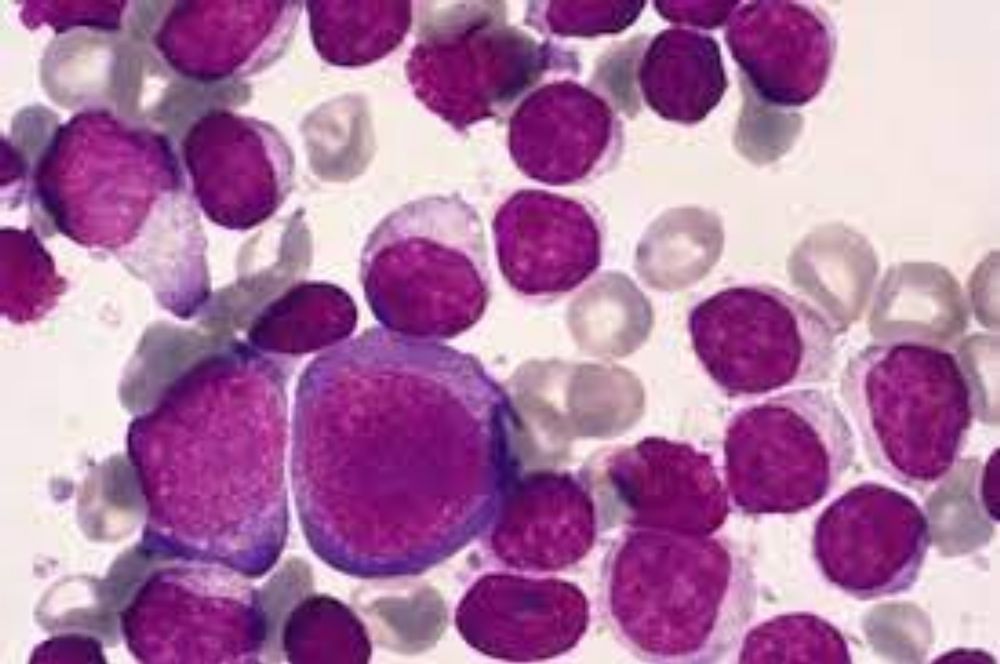
CHRONIC LEUKAEMIA :
Chronic leukemias are the type of leukemias in which the morphological substrate of tumor growth is more mature blood cells with a certain level of differentiation.
CCL is characterized by lymphoid hyperplasia of the hematopoietic organs [ lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow], as well as lymphoid infiltration of other organs and tissues. The spleen can weigh 1 to 3 kgs, but it can grow to be much larger over time. Hyperplasia of the lymphoid components is identified in the bone marrow punctuation; immature forms and Botkin- Humorecht bodies increase.
CHRONIC MYELOCYTIC LEUKAEMIA :
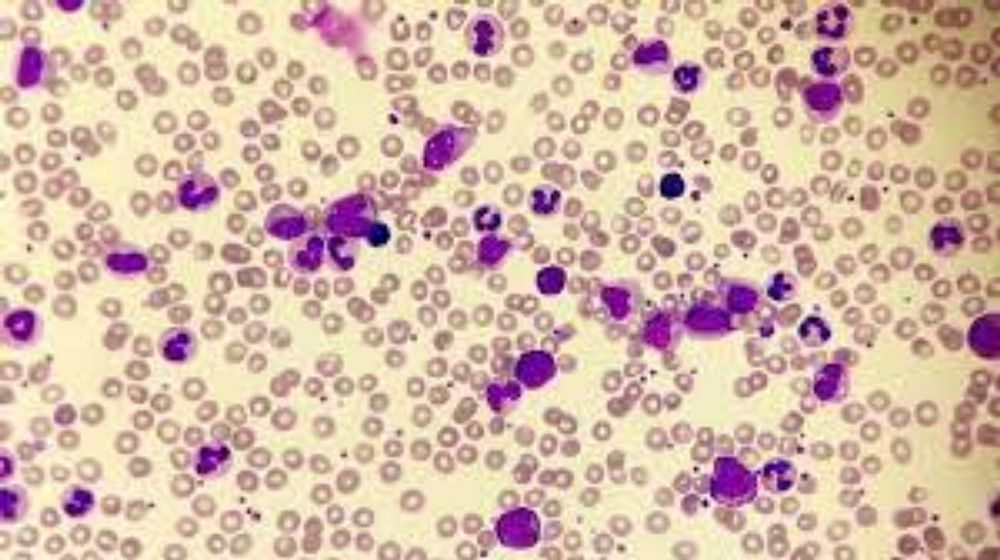
Chronic myelocytic leukemia is a systemic blood disease characterized by myeloid bone marrow hyperplasia caused by immature granulocytes whose maturation is inhibited, myeloid metaplasia of the spleen [dark red with ischemia, sclerosis, and hemosiderosis of the pulp], which can reach 3-6kgs; liver [grey-brown with leukemia infiltrations along with the sinuses. The bone marrow of flat bones, epiphyses, and diaphyses of the long bones is pus-like and grey-red[ pyoid].
Thank you for taking the time to read my blog. See you later….




