

Hello everyone!!!!
Today I will tell you about one of the primary tests we learn in Microbiology Laboratory in college.
We all are aware of basic cell structure. Outer layer of the cell is know as cell wall. Peptidogycan is major compound found in call wall which is basically composed of sugar and amino acid molecules. Thickness of the peptidoglycan in cell wall differentiate bacteria in two categories Gram Positive ( which has thick peptidoglycan layer about 50-90% of cell wall ) and Gram Negative ( which has thin peptigoglycan layer about 10% of cell wall ) as show in below picture .
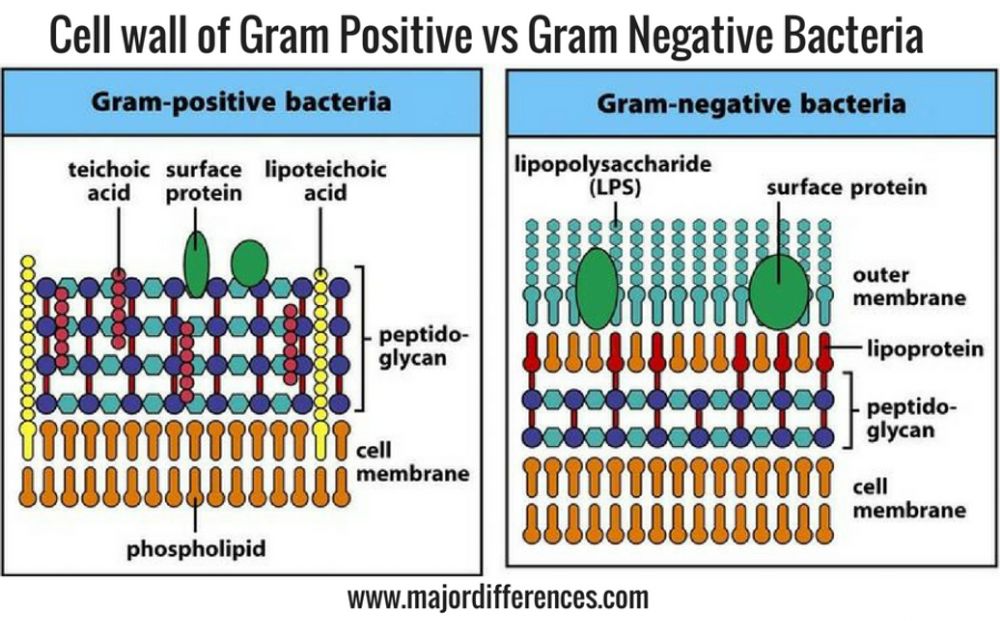
Mechanism of Staining -:
Crystal violet , first dye used in this staining penetrates into cell wall of both Gram positive and negative cells.positive ions of the dye interacts with negative ions in the membrane and cell wall gets stain in violet in colour.After adding iodine ion in it Crystal Violet Iodine complex (CVI) get form in the wall.
When decolorizer such as alcohol or acetone used in it, due multilayered nature of the peptidoglycan of Gram Positive cell,the CVI complex gets strapped and cannot remove by the addition of decolorizer. Hence Gram Positive Bacteria retain the stain and remain perple. Whereas in the case of Gram Negative bacteria, alcohol dissolves outer lipid area , leaving peptidoglycan layer exposed and it lead to removal of CVI complex making Gram Negative bacteria colourless.
A counter stain, basic fuchsin, stains the Gram Negative cells pink, differentiate them from purple Gram Positive bacteria.This test is important in characterization and classification of bacteria.It is also used in screening of infectious agent in clinical specimens.
Lets go for actual procedure of the staining -:
We get to observe something like this under microscope -:
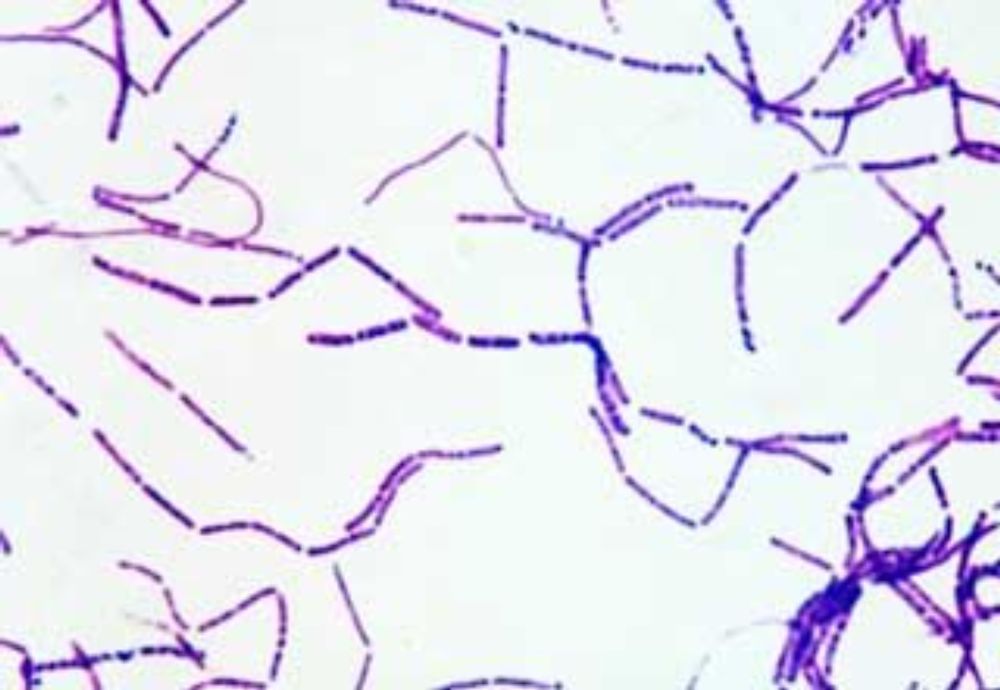
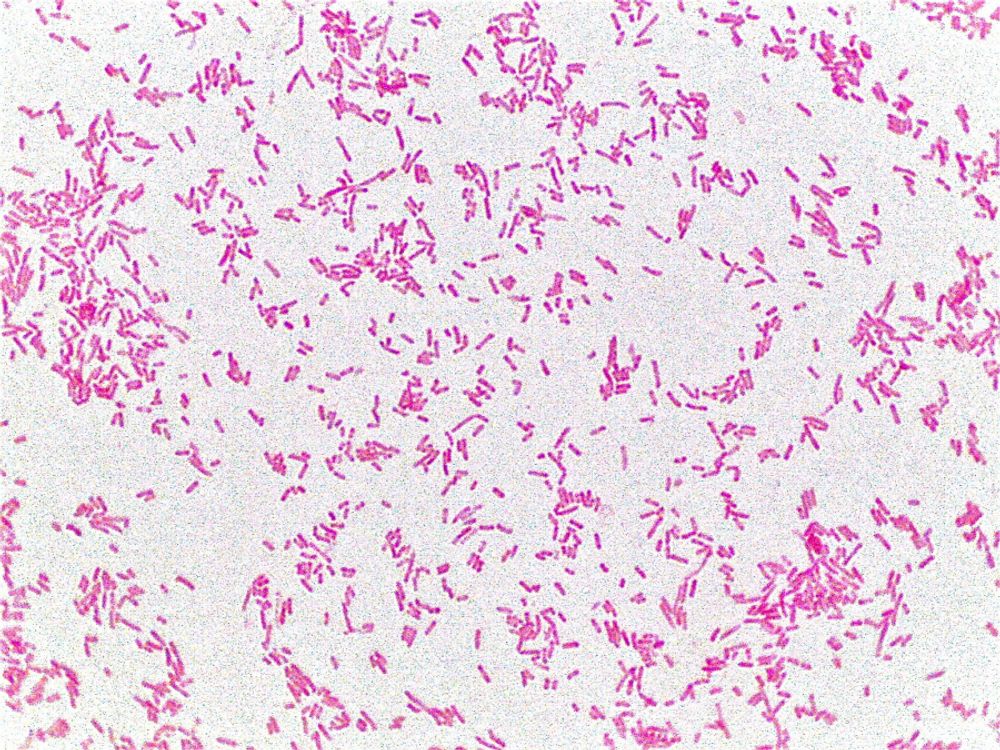
Do like, comment and share.
Suggestions are always welcome.






