
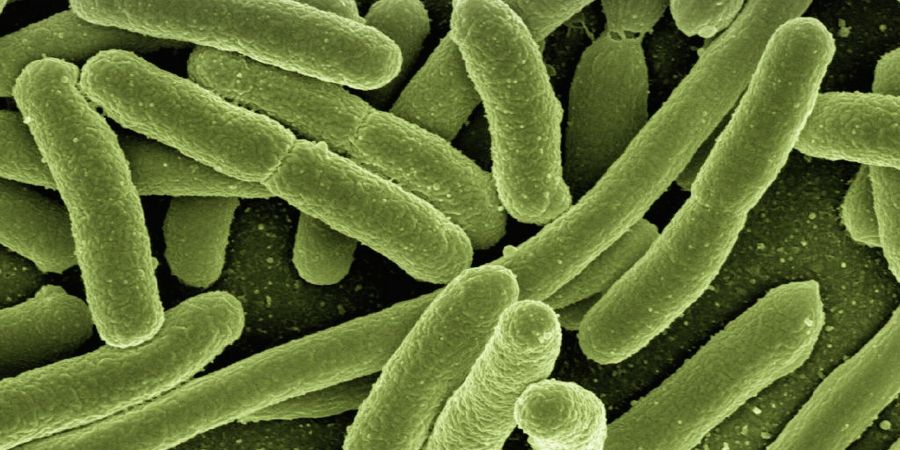
Bacterias are unicellular prokaryotic micro organisms. They have no chlorophil and no true branching.
Unit of measurement used in bacteriology is micron. Limit of resolution with the unaided eye is 200 micron. Size of medically important bacteria is 0.2 - 1.5 micron. Leewenhoek first observed bacteria using hand ground lenses
Bacteria have a distinct cell structure. Bacterial cell structure includes cell envelope, cell appantages and cytoplasm.
Bacterias have a very rigid cell wall amd gives shape to the cell. Its function is to prevent cell expansion and bursting due to water uptake. Cell wall constitute a significant portion of the dry weight of the cell and it is essential for bacterial growth and division. It cannot be seen by direct light microscope. It do not stain with simple stains. It may be demonstrated by the following
Chemically the cell wall is composed of peptidoglycon. Peptide formed by N acetyl glucosamine and N acetyl muramic acid, cross linked by peptide chains. Embedded in it are polyalcohol called Teichoic acid. Some are linked to lipids and are called Lipoteichoic acid. Lipoteichoic acid link peptidoglycan to cytoplasmic membrane and the peptidoglycan gives rigidity. The functions of Teichoic acid are :-
Outer membrane is found only in Gram negative bacteria, it functions as an initial barrier to the environment and is composed of lipopolysaccharide and phospholipids.
The lipopolysaccharide present on the cell wall of Gram negative bacteria account for their endotoxic activity and antigen specificity.
Flagella are long hair like helical filaments extending from cytoplasmic membrane to exterior of the cell wall. They are of four types
Some bacteria have the ability to form highly resistant resting stage called spores, which helps them to overcome adverse environmental conditions that are unfavourable for vegetative growth of cell.
