
Intoduction
Naegleria fowleri, named Cerebrum, eats one adaptable cell. single adaptable cell disease, south Naegleria is a one-celled critter, a solitary-celled creature, and only one of its animal categories, called Naegleria fowleri, can contaminate people.
Naegleria fowleri
Naegleria is a unicellular critter, a solitary-celled living being, and only one of its animal varieties, called Naegleria fowleri, can contaminate people, as per the US Communities for Infectious Disease Prevention and Counteraction (CDC). It was first found in Australia in 1965 and is generally found in warm freshwater bodies, like underground aquifers, waterways, and lakes.
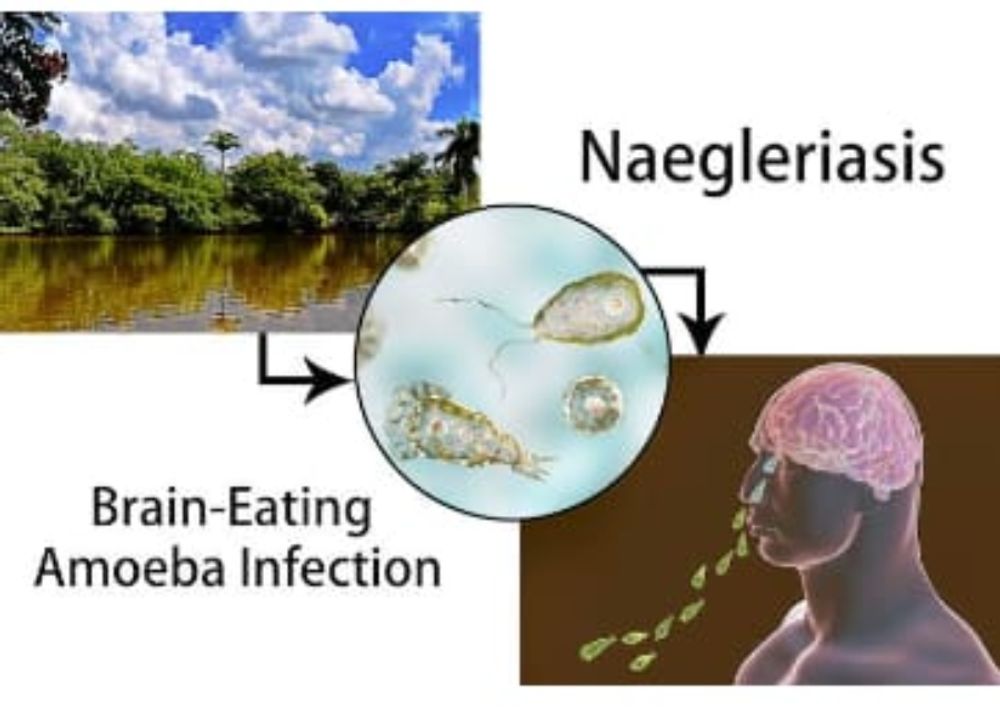
It contaminates people.
The single adaptable cell enters the human body through the nose and afterward makes a trip up to the mind. This can generally happen when somebody takes a dip, jumps, or, in any event, dunks their head in a freshwater body. Now and again, it was found that individuals got tainted when they cleaned their noses with sullied water. Researchers haven't found any proof of the spreading of Naegleria fowleri through water fumes or spray drops.
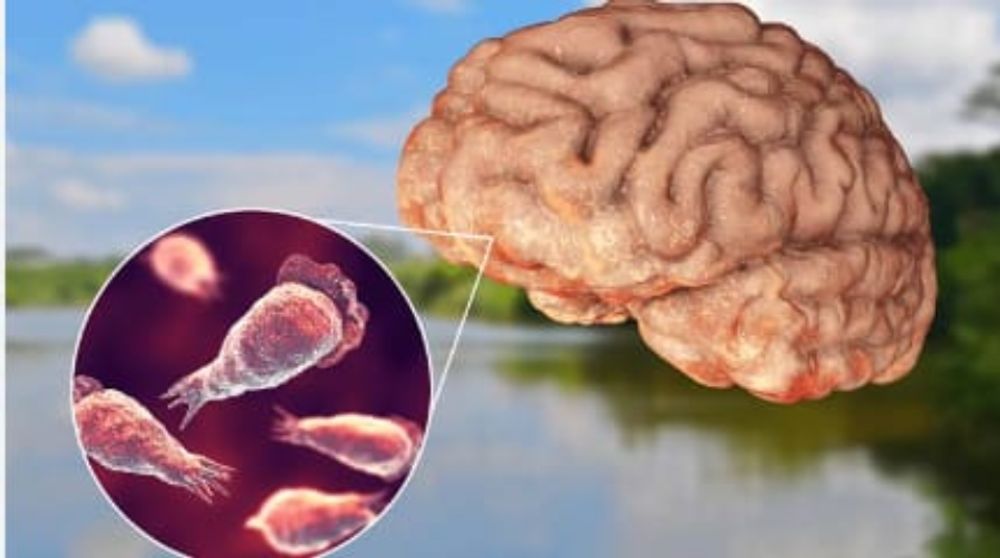
When Naegleria fowleri goes to the brain, it obliterates cerebrum tissues and causes a hazardous disease known as essential amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM), as per the CDC.
The side effects of PAM are :
The CDC says the main indications of PAM begin appearing one to 12 days after the disease.
In the underlying stages, they may be like meningitis, which is characterised by migraine, nausea, and fever. In the later stages, one can experience the ill effects of a solid neck, seizures, fantasies, and even a trance state. The disease spreads quickly, with normal cases lasting around five days.
Treatment for this contamination
As Naegleria fowleri contamination is uncommon and advances rapidly, researchers haven't had the option to distinguish any powerful medicines yet. As of now, specialists treat it with a mix of medications, including amphotericin B, azithromycin, fluconazole, rifampin, miltefosine, and dexamethasone.
Environmental change causes the spread of disease.
As per the CDC, with the climbing worldwide temperatures, the possibilities of getting Naegleria fowleri contamination will go up as the one-celled critter chiefly flourishes in warm freshwater bodies. The life form best in high temperatures up to 46 °C and, in some cases, can get by at significantly higher temperatures.
Reasons behind spreading
Different late examinations have found that an overabundance of barometric carbon dioxide has prompted an expansion in the temperature of lakes and waterways.
"These circumstances give the one-celled critter a better climate to develop." Heat waves, when air and water temperatures might be higher than expected, may likewise permit the single adaptable cell to flourish. Up until this point, Naegleria fowleri has been tracked down on all mainlands and proclaimed as the reason for PAM in the north of the world's 16 nations, including India.
