
Cancer is a large group of diseases
with one thing in common: They all
happen when normal cells become
cancerous cells that multiply and
spread.
Cancer is the second most common
cause of death in the U.S. But fewer
people are dying of cancer now than
20 years ago. Early detection and
innovative treatments are curing
cancer and helping people with
cancer live longer. At the same time,
medical researchers are identifying
independent risk factors linked to
developing cancer to help prevent
people from developing cancer.
Normally, cells follow instructions
provided by genes. Genes set down
rules for cells to follow, such as when
to start and stop growing. Cancerous
cells ignore the rules that normal
cells follow
Normal cells divide and multiply in
a controlled manner. Cancerous
cells multiply uncontrollably.
Normal cells are programmed to
die (apoptosis). Cancerous cells
ignore those directions.
Normal cells for solid organs stay
put. All cancerous cells are able to
move around.
Normal cells don't grow as fast as
cancerous cells.
Cancer starts when a gene or several
genes mutate and create cancerous
cells. These cells create cancer
clusters, or tumors. Cancerous cells
may break away from tumors, using
your lymphatic system or
bloodstream to travel to other areas of your body.
For example, a tumor in your breast
may spread to your lungs, making it
hard for you to breathe. In some types
of blood cancer, abnormal cells in
your bone marrow make abnormal
blood cells that multiply
uncontrollably. Eventually, the
abnormal cells crowd out normal
blood cells.
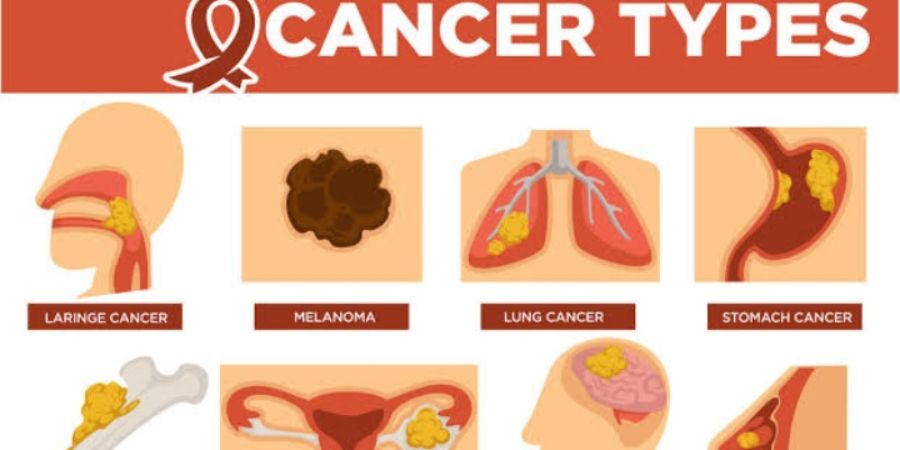
According to the American Cancer
Society,1 in 2 men and people
assigned male at birth (AMAB) and 1
in 3 women and people assigned
female at birth (AFAB) will develop
cancer. As of 2019, more than 16.9
million people in the U.S. were living
with cancer. The most common
cancers in the United States are:
Breast cancer: Breast cancer is
the most common type of cancer.
It mostly affects women and
people (AFAB). But about 1% of all
breast cancer cases affect men
and people (AMAB).
Lung cancer: Lung cancer is the
second most common cancer.
There are two types of lung
cancer: non-small cell cancer and
small cell lung cancer.
Prostate cancer: This cancer
affects 1 in 9 men and people
AMAB
Colorectal cancer: Colon cancer
and rectal cancer affect different
parts of your digestive system.
Blood cancers: Leukemia and
lymphoma are the most common
blood cancers.
Cancer is a complicated disease. You
can have cancer for years without
developing symptoms. Other times,
cancer may cause noticeable
symptoms that get worse very
quickly. Many cancer symptoms
resemble other, less serious
illnesses. Having certain symptoms
doesn't mean you have cancer. In
general, you should talk to a
healthcare provider anytime there'sa
change in your body that lasts for
more than two weeks.
