
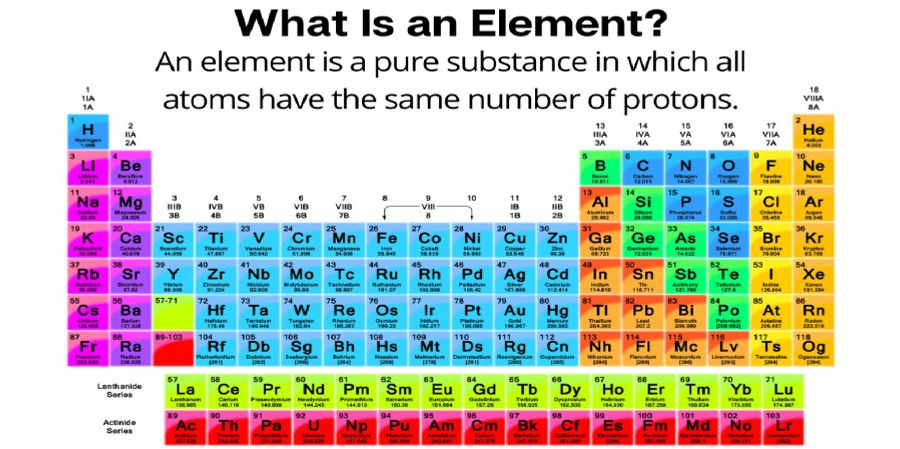
Wouldn't it be ideal to melt in your mouth and carry its deliciousness with your tongue? In chemistry, an element is a component that connects atoms with the same number of protons in an atomic nucleus. Unlike compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simple substances by chemical reactions. Usually Currently 118 compounds are known. About 20% of these are unnatural (or only available in small quantities) and are known only because they are synthetically manufactured in the laboratory. Of the known compounds, 11 (hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, and 6 rare gases) are gases under normal conditions, 2 (bromine and mercury) are liquids (2 more, cesium). And gallium, these are close to cesium and gallium, or just above (at room temperature), some are solid. It can gather together to form a complex system called a compound. The number of possible combinations is endless. Perhaps millions are known and some are discovered every day. Compounds, they lose their unique identity, and the product has properties that are completely different from the binding it, for example, very different properties. The hydrogen gas and the of oxygen can be combined to form oxygen or water with completely different properties from hydrogen. Water is clearly not a substance as it contains hydrogen and oxygen and can actually be chemically converted into two compound's. However, these two substances are element's because they cannot be broken down into simple substances by known chemical processes. Many samples of naturally occurring substances are visible mixtures of that. For example, seawater is a mixture of water and many others, the most common of which is sodium chloride or a common salt. It differ from compounds in that they can be broken down into components by a physiological process. For example, a simple evaporation process separates water from certain in seawater. Atomic theory, often referred to as the Greek philosopher Democritus, was considered to consist entirely of four-element atoms: Earth, air, fire, and water. However, Aristotle's notion of progressive concepts was commonplace and influenced thinking until 16th-century experiments forced the revival of the notion of atoms. Two sets of experimental evidence support atomic theory. The first is the detailed behavior of gaseous substances and the second is the relative mass to the chemical composition. British chemist John Dalton first explained the dynamic laws of chemical reactions in the theory of the existence of atoms with different structures. At that time, chemical bonds (valences) and their associated atomic weights were very interesting. Since then, many independent tests have been conducted to confirm the atomic hypothesis and are now accepted worldwide. In fact, in 1969, isolated uranium and thorium atoms were detected using an electron microscope. Any member of a chemical group containing earth 3 groups of 3 elements (scandium [Sc], yttrium [Y], and lanthanum [La])


