
The diagnosis of parasitic infection is done by
Clinical symptoms
Laboratory diagnosis
Purposes of performing laboratory diagnosis is
Confirmation of clinical diagnosis
Identification of clinically undiagnosed infection
Specimen collected for laboratory diagnosis specimen is collected depending on the type of parasitic infection suspected
Stool
Blood
Serum and plasma
Tissue and aspirate
Other specimen like sputum, urine,anal swab, duodenal aspirate, urogenital specimen
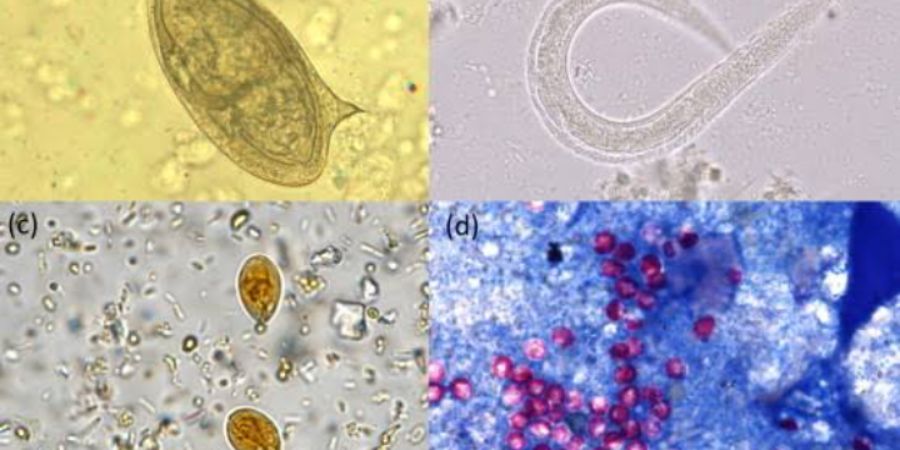
Stool examination
Sample collection
The stool sample is collected in a clean and dry container
It should not be mixed with urine or disinfectant
Specimen can be obtained by enema or laxative
Sometimes use of preservatives may be indicated
Examination of the stool sample
Gross examination
Consistency should be noted.The stool may be liquid, formed or semiformed.sometimes the gross examination may reveal the type of parasitic infection e,g mucoid blood stained some parasite can be detected macroscopically in the stool sample e.g ascaris
Microscope examination
Saline mount, iodine mount,the Saline and iodine wet mount help in the identification of protozoa,cyst, eggs and larva of helminth and crystal
Permanent stained smears
Iron haematoxylin
Wheatleys trichrome stain
Modified ziehl neelsan stain
Concentration method are done in case where the parasite are scanty in the specimen
Floatation techniques are solution which have High specific gravity eggs and cyst will float and the other debris will sink
The important agent used are
Saturated sodium chloride
Zinc sulphate centrifuge floatation
Sedimentation techniques are solution which have low specific gravity
The most commonly used is formol ether
Antigen detection
Fresh or preserved stool sample are used for antigen detection
There are several commercial ELISA kita for diagnosis of amoebiasis
Direct immunofluorescence assay is done for giardia cyst
Molecular diagnosis
The polymerased chain reaction is used for identification of parasites in the stool sample the amplified fragments can be further analysed by using restrictions fragments length polymorphism or by dna sequence
Blood examination
The blood samples that are collected are
Fresh capillary blood of finger
Venous blood collected in edta
Blood samples will be used for
Microscopic examination thin smear thick smear wet mount for microfilaria
Thick smear
Used to screen a large amount of blood
Another advantage is that it can be stained later
Thin smear
It is used to examine malarial parasite in the RBC thin smear help in th identification of plasmodium species
Molecular diagnosis1 to 5 ml blood samples is collected in tube with edta dna is extracted usin5dna extraction kits
Used to identify the plasmodium species




